Treatments
Kidney and Bladder Stones
Forms due to a mineral deposit accumulating in the kidney or bladder.
Causes: Bladder stones start to grow when urine is left in the bladder after urinating. This is often due to an underlying medical condition that stops the bladder from completely emptying when using the toilet.
Symptoms: Bladder stones may not produce symptoms straight away. But, if the stone irritates the bladder, symptoms can include the following:
- Discomfort or pain in the penis for males
- More regular urination or a stop-start flow
- Starting a stream during urination takes longer
- Pain in the lower stomach area
- Pain and discomfort when urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Cloudy or abnormally dark urine
Treatments:If bladder stones are caught when they are still small, simply increasing the amount of water the individual drinks can be enough to pass them naturally. If they are too large to pass in the urine, treatment for bladder stones normally involves either breaking them up or removing them by surgery.
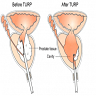
TUIP/TURP
The removal of the prostate which is enlarged. This is done by inserting a scope through the urethra and the cutting or resecting the prostate.
Causes: Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP) is a procedure to treat urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate. It's generally used for men with small- to moderated-sized prostates.
Symptoms:
- Frequent, urgent need to urinate
- Difficulty starting urination
- Slow (prolonged) urination
- Increased frequency of urination at night
- Stopping and starting again while urinating
- The feeling that you can't completely empty your bladder
- Urinary tract infections
Treatments:The most common treatment is through surgery. Your doctor removes portions of the prostate that are affecting your urine flow. There is no cutting and no external scars are seen since a scope is inserted thorough the urethra to remove the excess tissue. With TURP, some men might get what’s called “retrograde ejaculation,” (ejaculation of semen into the bladder instead of through the urethra).
Urinary Tract infection
Generally treated with antibiotics and more prevalent in women. Caused by bacterial infection in urethra and/or bladder but can spread to kidney and become dangerous. Usual signs are pain in urination, blood in urine, increased frequency of urination. Occasionally could result in fever.
Causes: It typically occurs when bacteria enters the urinary tract via urethra and begin to multiply in bladder. A majority of UTIs are caused by bacteria E.coli. Mycoplasma and Chlamydia can infect urethra, not the bladder.
Symptoms: To identify UTI, keep an eye on:
- Pain in lower abdomen, groin, pelvis or bladder
- Pain can occur during intercourse or urination
- Vaginal irritation or cramping
- Foul smelling of urine
- Bladder spasm
- Dark urine
- Persistent urge to urinate
- Blood in urine
- Frequent urination
- Cloudy urine
- Sense of incomplete bladder emptying
Treatments:The most common treatment consists of antimicrobes and antibiotics, which stops the growth of the bacteria or kill it. You can also adopt some self-care techniques like urinating after intercourse, drink lost of water and urinate frequently as this will help bacteria to flush out from the body. A variety of pain relief medications may be prescrbed to alleviate pain. Applying heating pad to back or abdomen can also help.

Erectile Dysfunction Treatment
A problem involving maintaining an erection, premature or delayed ejaculation, or pain with erection. Treated with diagnostic testing and a variety of treatments.
Causes: Some of the causes of erectile dysfunction are:
- High cholestrol
- Diabetes
- Tobacco use
- Sleep disorder
- Mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, stress
- Alcoholism
- Metabolic syndrome
- Heart disease
- Relationship problems due to poor communcation, stress or other concerns, and much more
Symptoms: A man's inability to keep or get an erecton firm enough for intercourse. It is usually self-diagnosable. People may experience trouble maintaining or getting erection, soft erections.
Treatments:The treatment might vary from person to person. They are first evaluated for any psychological or physical conditions. If it doesn't help, assistive devices and medications are used for treatment.

Vasectomy
This is a voluntary sterilization procedure for men. The vas deferens is cut and the tube that sperm travels through is no longer connected, so sperm is no longer present in seminal fluid. Reversion is possible but difficult, so vasectomy should be considered permanent.
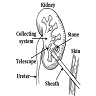
Laparoscopic Urological Surgeries
Involves a wide variety of procedures and is minimally invasive. Examples of procedures are pyeloplasty, nephrectomy, radical nephrectomy, vesicovaginal fistula repair, ureteric reimplantation, and bladder/ureter stone diverticula excision.